Lab manager
Dr Mauro Rubino
General Overview of the methodology
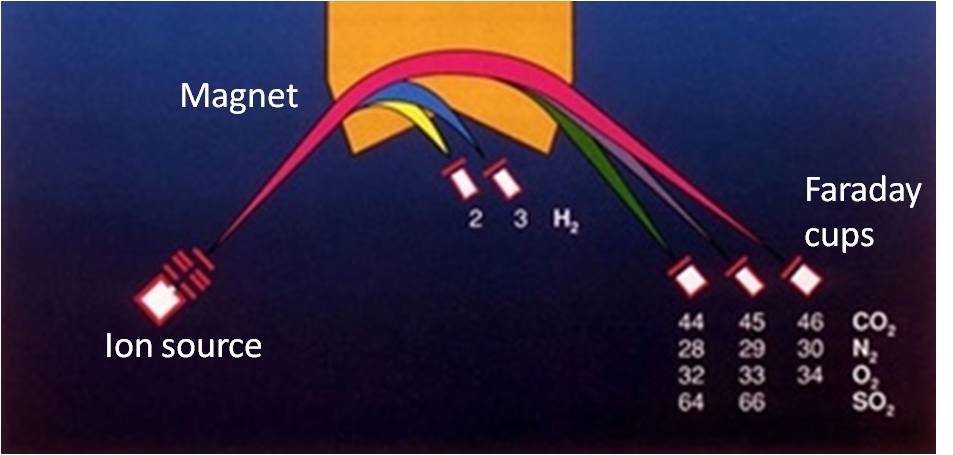
Mass spectrometers can be briefly described as follows:
• an electron impact ion source (preparation) producing positive ions which are accelerated by electric fields and separated by
• a magnetic selection (analysis) with double focusing magnet which separate the ions with different masses that are then measured on
• an array of Faraday Cups (detection) for simultaneous measurement of masses 1,2 for H2 or 44,45,46 for CO2 or 32,33,34 for O2 or 28,29 for N2 or 28,29,30 for CO and 64,66 for SO2.
Generally, the ion source of an IRMS system accepts gaseous samples only. Therefore, the molecules whose isotopic ratio is measured (H2, CO2, N2, CO and SO2) can be produced
• offline in external preparation lines and injected in the IRMS through a Dual Inlet system, or
• online by means of peripherals (Elemental Analyser, Thermal Combustion, Gas Chromatography, Gas bench) and injected through a CONFLO (Continuous Flow) interface.
Laboratory equipment
At the CIRCE IRMS laboratory, there are 3 (three) ThermoFisher mass spectrometers
• 1 Thermo Quest Delta plus
• 2 Thermo Fisher Delta V advantage
for the measurement of 2H/1H, 12C/13C, 14N/15N, 18O/16O and 34S/32S.
The following peripherals are available:
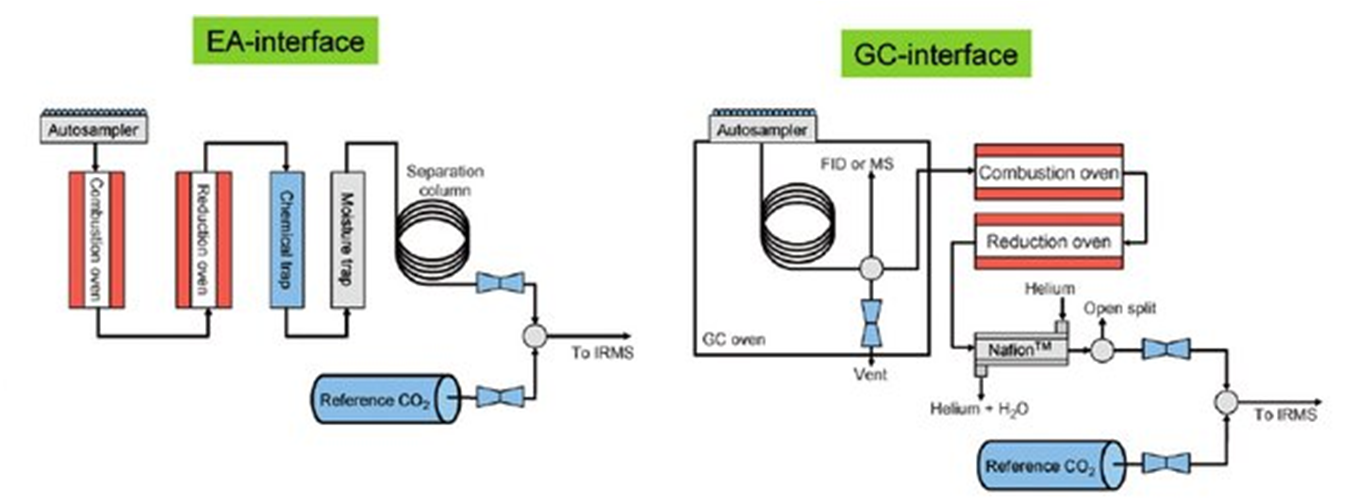
• 2 EA (Elemental Analysers) producing CO2, N2 and SO2 through combustion of solid and liquid samples for analyses of C, N and S isotopes;
• 2 TC/EA (Thermal Combustion/Elemental Analyser) producing CO, N2 and H2 through pyrolysis of solid and liquid samples for analyses of O, N and H isotopes;
• 1 GC/C-TC (Gas Chromatograph/Combustion-Thermal Combustion) separating specific compounds in a mixture and then producing either CO2, N2 and SO2 through combustion or CO, N2 and H2 through pyrolysis for C, N, H, O and S isotope analyses;
• 1 Gas bench for the analysis of H and O isotope analyses in water samples, C and O isotope analyses in Dissolved Inorganic Carbon and Carbonates, and C and O isotope analyses in ambient air CO2.
On line (continuous flow) coupling of peripherals and IRMS are performed via CONFLO interfaces (CONFLO II, III and IV) which reduce the working pressure and connect the peripherals (tipical operating pressure = 1 atm) with the IRMS source (tipical operating pressure 10-6-10-8 mbar) by means of the open split technology.

Main applications carried out at the IRMS lab
Environmental pollution - Hydrology
Contamination of water resources from landfill leachate
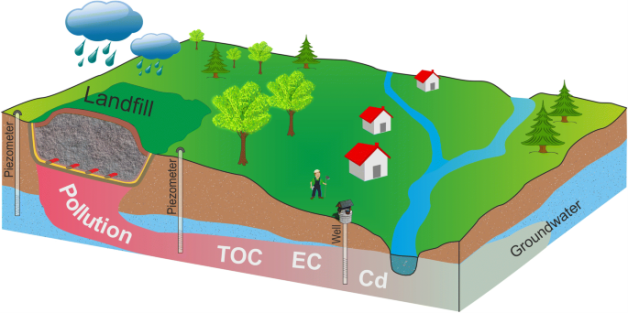
Municipal landfills impact on ground and surface water resources. Whene they are often located in industrial areas, where there are other sources of contamination (e.g. incinerators and oil refineries), the analysis of natural isotopes of CO2, CH4 and leachate can help identify the contamination by leachate from the landfill because of the characteristic isotope signature of gas and leachate. In the IRMS laboratory at CIRCE, water samples from landfill sites (e.g. Malagrotta near Rome) have been investigated by means of D and 18O measurements. Further work with 13C of DIC (Dissolved Inorganic Carbon) is underway.
Nitrate (NO3-) contamination of groundwater
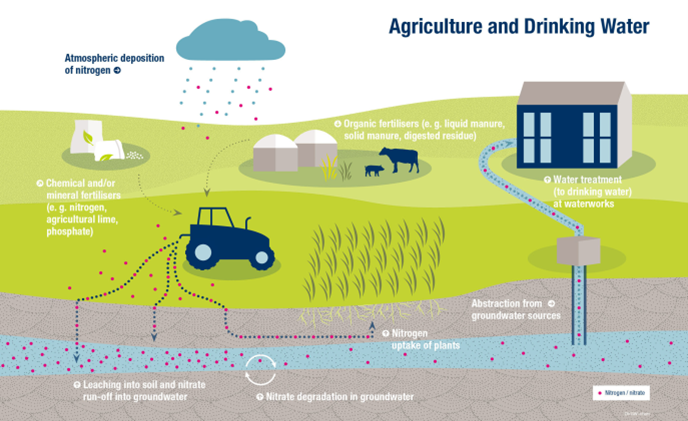
Shallow aquifers worldwide can be contaminated by NO3- leached from soils exploited by intensive agriculture or from leaks of the sewage system in densely populated areas. The development of remediation plans for polluted areas requires the identification of the sources of NO3- in water bodies. At CIRCE IRMS lab, the apportionment of NO3- contamination sources in shallow groundwater in five regions of the Po River basin has been carried out measuring nitrogen and oxygen isotopic ratios of dissolved nitrate (15N and 18O).
Environmental pollution - Atmospheric Science

The identification of the sources of atmospheric pollution can be performed through measurements of isotopic composition. Particulate matter, for example, is composed of many molecules and atoms having different origins. The IRMS laboratory at CIRCE is involved in an experiment aiming to identify the sources of C and N in particulate matter samples in Naples. Dual measurements of 15N and 13C can help quantify the proportion of N and C derived from different sources of pollution (cars and bus exhausts, private houses, pizza fire oven, etc...). This is essential to develop appropriate remediation strategies.
Materials Science

Isotope methodologies guarantee high sensitivity in the quantification of tracers in the "micro" range. The technique called Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry (IDMS) represents the only method for the analysis of elements in concentration of a few % down to ultra trace (i.e. < ng kg-1). Basically, small quantities (traces) of an element can be quantified via measurements of isotopic ratios combined with the introduction of an isotopic spike. As an example, the IRMS lab at CIRCE is a key player in testing the detection elements of the KM3net experiment (https://www.km3net.org/) for leaks in a hyperbaric chamber.
Archaeometry

Isotopic methodologies can support archaeological sciences because they can provide information about the age and origin of ancient materials and deposits. Analyzing human remains for their C, N, O, isotopic signatures (the so-called isotopic fingerprints), one can study the dietary habits of an individual or group, determine where a person grew up or where they lived in the last years of their life. At the IRMS lab, analyses of charred grains from Turkey helped infer information about the usage of agricultural practices.
Food traceability

Isotopic analyses of foods have become a widespread tool to evaluate the quality, authenticity and origin of labelled products. Wines, alcoholic beverages and fermented fruit juices are distilled to produce ethanol. The ethanol of a number of wine samples has been analyzed at the IRMS lab at CIRCE for O and C isotope composition in order to detect exogenous sugar added during the fermentation to increase the alcohol grade of the wine.

